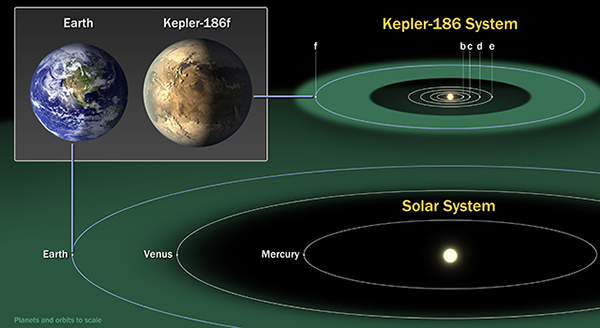
Using NASA’s Kepler Space Telescope, astronomers have discovered the first Earth-size planet orbiting a star in the ”habitable zone” — the range of distance from a star where liquid water might pool on the surface of an orbiting planet.
The discovery of Kepler-186f confirms that planets the size of Earth exist in the habitable zone of stars other than our sun.
While planets have previously been found in the habitable zone, they are all at least 40 percent larger in size than Earth, and understanding their makeup is challenging. Kepler-186f is more reminiscent of Earth.
”The discovery of Kepler-186f is a significant step toward finding worlds like our planet Earth,” said Paul Hertz, NASA’s Astrophysics Division director at the agency’s headquarters in Washington. ”Future NASA missions, like the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite and the James Webb Space Telescope, will discover the nearest rocky exoplanets and determine their composition and atmospheric conditions, continuing humankind’s quest to find truly Earth-like worlds.”
Jeremy Kasdin: The flower-shaped starshade that might help us detect Earth-like planets
Astronomers believe that every star in the galaxy has a planet, one fifth of which might harbor life. Only we haven’t seen any of them — yet. Jeremy Kasdin and his team are looking to change that with the design and engineering of an extraordinary piece of equipment: a flower petal-shaped ”starshade” that allows a telescope to photograph planets from 50,000 kilometers away. It is, he says, the ”coolest possible science.”

 NewsVoice är en nättidning för oberoende nyheter, debatt och analys.
NewsVoice är en nättidning för oberoende nyheter, debatt och analys. 
